Per operare in un ambiente di lavoro sicuro, è fondamentale che progettisti e costruttori di macchine e impianti abbiano un’adeguata conoscenza delle esigenze legislative da rispettare nei limiti delle proprie responsabilità.
The EU 1025 regulation of the European Parliament and Council dated 25 October 2012 on the matter of European standardization states that by standard they intend:
“standard’ means a technical specification, adopted by a recognised standardisation body, for repeated or continuous application, with which compliance is not compulsory, and which is one of the following”
International standard
Means a standard adopted by an international standardisation body
European standard
Means a standard adopted by a European standardisation organisation
Harmonised standard
Means a European standard adopted on the basis of a request made by the Commission for the application of Union harmonisation legislation.
National standard
Means a standard adopted by a national standardisation body
Therefore, standards represent those documents which define the state fo the art characteristics of a product or service (dimensions, performance, environment, quality, organization etc.) and are the result of the work of thousands of experts in Italy and worldwide.
ISO, UNI and IEC standards
The most authoritative body worldwide is ISO – International Organization for Standardization – which determines the technical regulations, assessments,inspection and standardization of quality processes in prductiove environments.
ISO merges the standardization bodies of 157 industrialized countries and developing countries worldwide.
In Italy ISO standards worldwide and CEN (European Committee of Norms) at European level are repesented by the non profit private organization UNI (Italian National Body of Unification).
UNI looks after the normative aspects for industrial, commercial and third sector businesses.
ISO cooperates closely with IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission ): this international organization is responsible for the standard description in the matter of electricity, electronics and connected technologies. UNI’s main goal is to divulge technical standards and support their balance.
European standards for machinery safety
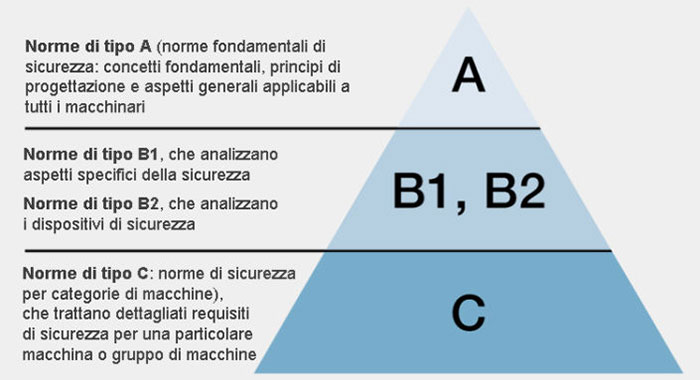
The current European standards for machinery safety is divided into 3 types:
A type standards
These basic standards give basic concepts, principles for design, and general aspects that are applicable to machinery
B type standards
These generic safety standards deal with one safety aspect or one type of safeguard, which can be used across a wide range of machinery.
Type-B includes two subdivisions:
- Type-B1 standards focus on particular safety aspects (safety distances, surface temperature, or noise)
- Type-B2 standards are for safeguards (two-hand controls, interlocking devices, pressure sensitive devices, fixed and movable guards, photcell barriers)
C type standards
These documents handle detailed safety guidelines for a particular machine or group of machines.



